Network Signal Encoding Methods
NRZ
Map the data value 1 onto the high signal and the data value 0 onto the low signal.
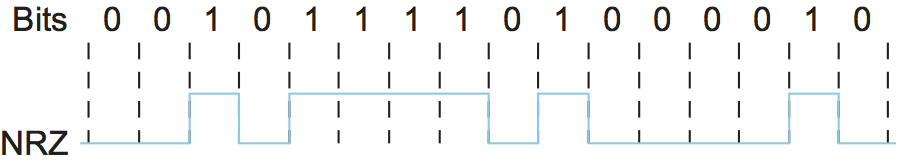
cons: baseline wander and not able sync clock
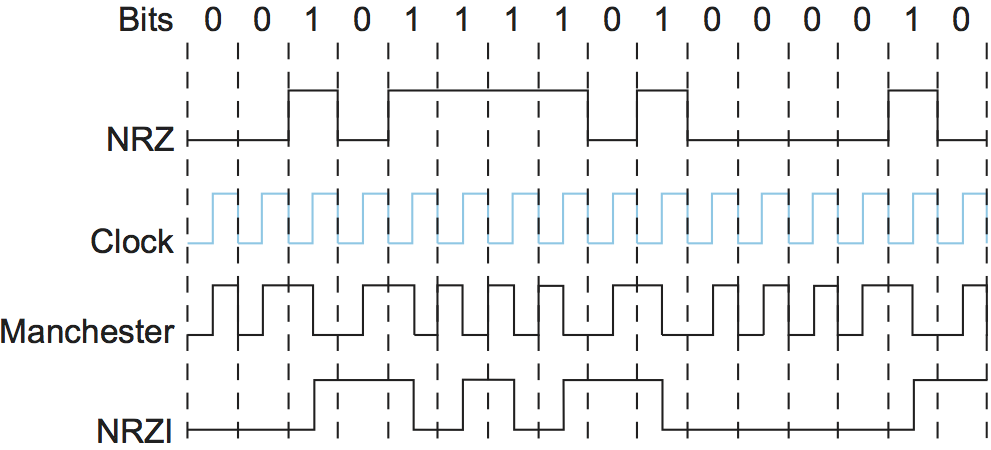
NRZI
Make a transition from current signal to encode a 1 and stay at current signal ecode a 0. This solves the consecutive 1s, but does noting to consecutive 0s.
Manchester
Merging the clock with the signal by transmition the exclisive OR of the NRZ and clock. It doubles the rate at which signal transistions are made on.
4B/5B
The idea is to insert extra bits into the bit stream so as to break up long sequences of 1s or 0s. The 5-bit codes are selected in such a way that each one has no more than one leading 0 and no more than two trailing 0s.